Chrome Write-up - TryHackMe
Extracting Chrome credentials that were encrypted with DPAPI.
Chrome is a hard room on TryHackMe. It’s all about tracing the attacker’s steps to find out what they did.
Starting with Wireshark
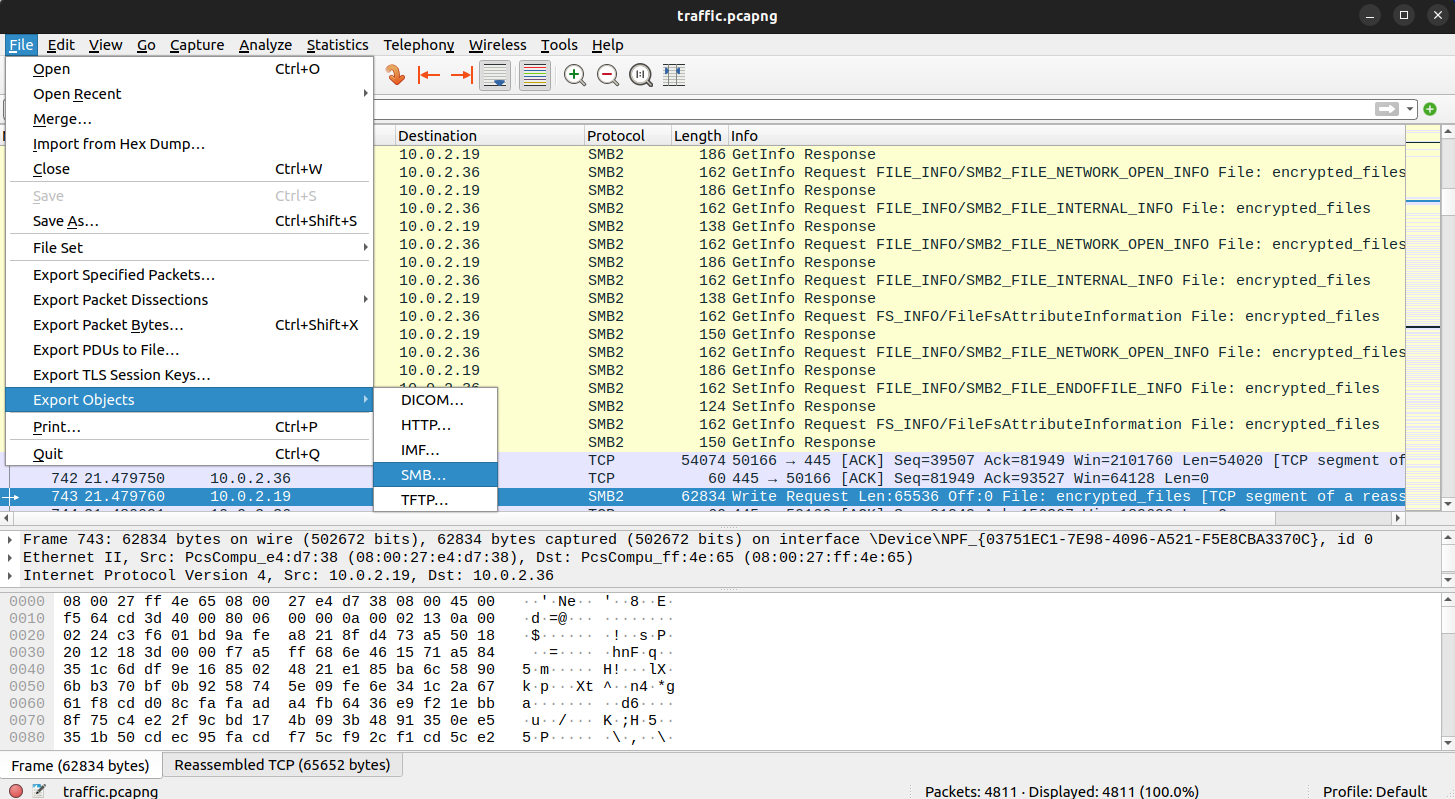
First, I downloaded the .pcap file and opened it in Wireshark. I noticed that the attacker transferred two files via SMB.
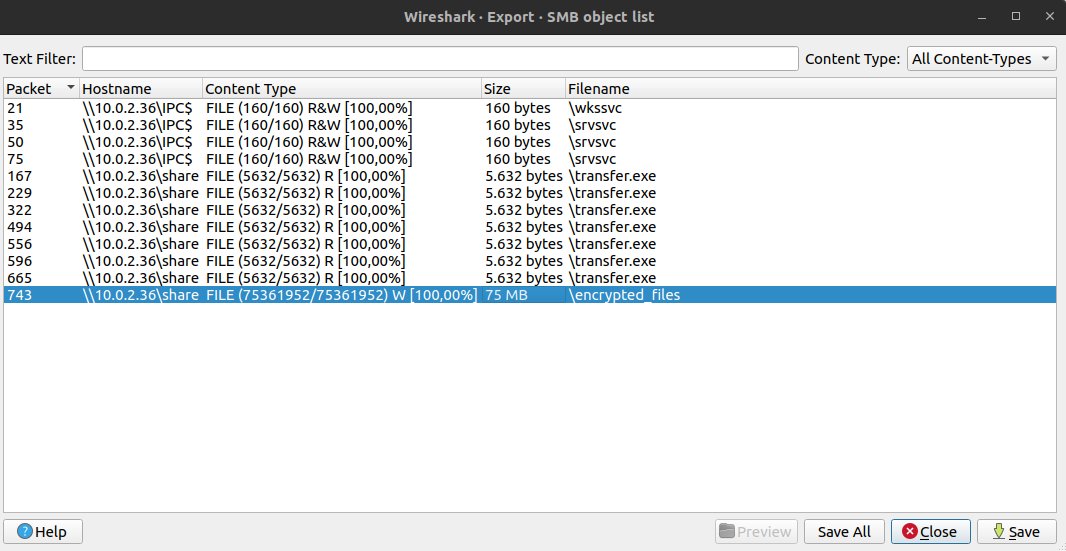
File -> Export Objects -> SMB -> Save All
Two files were transferred: transfer.exe and encrypted_files.
Reverse Engineering transfer.exe
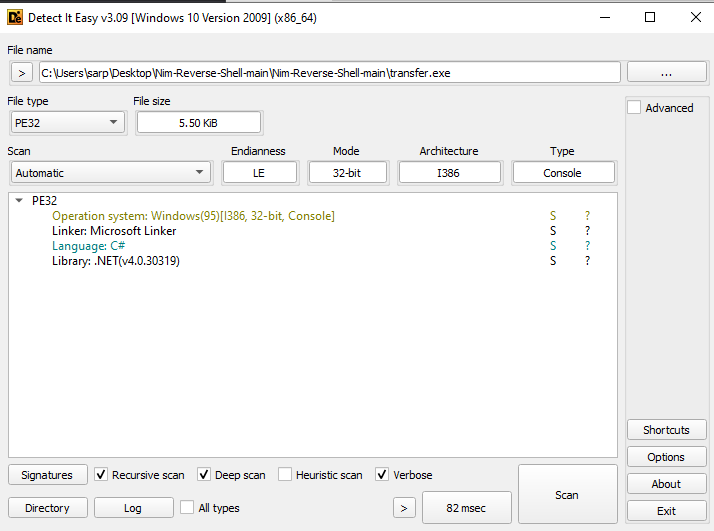
Using Detect It Easy, I found out that the file is a .NET executable.
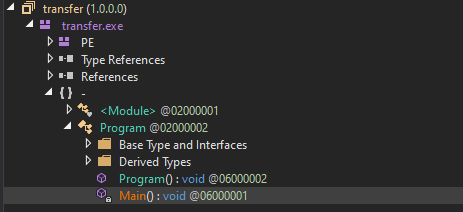
With dnSpy, I decompiled the file and reached the source code.
Here’s the source code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
// Token: 0x02000002 RID: 2
public class Program
{
// Token: 0x06000001 RID: 1 RVA: 0x00002050 File Offset: 0x00000250
private static void Main()
{
try
{
byte[] bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("PjoM95MpBdz85Kk7ewcXSLWCoAr7mRj1");
byte[] bytes2 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("lR3soZqkaWZ9ojTX");
string text = "C:\\Users\\hadri\\Downloads\\files.zip";
byte[] array = File.ReadAllBytes(text);
byte[] array2;
using (Aes aes = Aes.Create())
{
aes.Key = bytes;
aes.IV = bytes2;
ICryptoTransform cryptoTransform = aes.CreateEncryptor(aes.Key, aes.IV);
using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
using (CryptoStream cryptoStream = new CryptoStream(memoryStream, cryptoTransform, 1))
{
cryptoStream.Write(array, 0, array.Length);
}
array2 = memoryStream.ToArray();
}
}
string text2 = "C:\\Users\\hadri\\Downloads\\encrypted_files";
File.WriteAllBytes(text2, array2);
Console.WriteLine("File encrypted and saved successfully.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: " + ex.Message);
}
}
}
Since we have the encryption key and the IV, we can decrypt the encrypted_files file.
Here’s the Python script to decrypt the file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def decrypt(key, iv, ciphertext):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
return cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
encrypted = open('encrypted_files', 'rb').read()
key = b'PjoM95MpBdz85Kk7ewcXSLWCoAr7mRj1'
iv = b'lR3soZqkaWZ9ojTX'
decrypted = decrypt(key, iv, encrypted)
open('decrypted_files.zip', 'wb').write(decrypted)
After running the script, I extracted the decrypted_files.zip file.
Extracting decrypted_files.zip
The attacker had compressed the %APPDATA% folder.
The contents of the folder were:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
C:\Users\sarp\Downloads>tree decrypted_files
Folder PATH listing
Volume serial number is 000000A2 3CD9:FFF3
C:\USERS\SARP\DOWNLOADS\DECRYPTED_FILES
└───AppData
├───Local
│ └───Google
│ └───Chrome
│ └───User Data
│ └───Default
└───Roaming
└───Microsoft
└───Protect
└───S-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001
The challenge was to extract the Chrome credentials from the Login Data file. However, we can’t just use Login Data and Local State files because the Local State file is encrypted with DPAPI.
Decrypting Local State
The bad news is to decrypt the Local State file, we need the user’s password. Good news is we have sid-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001, which makes it possible to bruteforce the password.
Let’s use DPAPImk2john and john to crack the password.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Desktop]
└─$ DPAPImk2john --sid="S-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001" --masterkey="8c6b6187-8eaa-48bd-be16-98212a441580" --context="local" > hash.txt
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Desktop]
└─$ cat hash.txt
$DPAPImk$2*1*S-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001*aes256*sha512*8000*46bc22dbffb7cfe4cfc5895acf364a94*288*a332e98ce791b7416157137e7193596d4594dc599acc321f6ed9e94a818879461639b958099ab61361c7fd4d6668ca2d8995488ffba78758b945dcbfc60498c84b14c8021fbee8d90cf4165637222c8a6cd1eb3c5a85acf85177b1ec86240c7e077eb5e427e27832f3481664baf54c06cb3bb47bcfc253620958f02f69bc98ece8e51b6ef3c498047efb4a2b57bf804b
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Desktop]
└─$ john --wordlist=rockyou.txt hash.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (DPAPImk, DPAPI masterkey file v1 and v2 [SHA1/MD4 PBKDF2-(SHA1/SHA512)-DPAPI-variant 3DES/AES256 256/256 AVX2 8x])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 8000 for all loaded hashes
Will run 2 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
bubbles (?)
Here we go! The password is bubbles.
Proceeding with Mimikatz:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # dpapi::masterkey /in:"C:\Users\sarp\Downloads\decrypted_files\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Protect\S-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001/8c6b6187-8eaa-48bd-be16-98212a441580" /sid:"S-1-5-21-3854677062-280096443-3674533662-1001" /password:bubbles /protected
**MASTERKEYS**
dwVersion : 00000002 - 2
szGuid : {8c6b6187-8eaa-48bd-be16-98212a441580}
dwFlags : 00000005 - 5
dwMasterKeyLen : 000000b0 - 176
dwBackupKeyLen : 00000090 - 144
dwCredHistLen : 00000014 - 20
dwDomainKeyLen : 00000000 - 0
[...]
[masterkey] with password: bubbles (protected user)
key : ca4387eb0a71fc0eea23e27f54b9ae240379c9e82a05d6fca73ecee13ca2e0e4d98390844697d8ed10715415c56152653edf460a47b70ddb868a03ee6a3f9840
sha1: 217522c457cfe8a95da45da81d6b898080e2067d
Bingo! We have the masterkey. Now, let’s decrypt the Local State file.
We only need the encrypted data from the Local State file, not the entire file. Here’s the Python script to extract it:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
import json
import base64
fh = open('Local State', 'rb')
encrypted_key = json.load(fh)
encrypted_key = encrypted_key['os_crypt']['encrypted_key']
decrypted_key = base64.b64decode(encrypted_key)
open("dec_data",'wb').write(decrypted_key[5:])
Now pass the dec_data file to mimikatz:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
mimikatz # dpapi::blob /masterkey:ca4387eb0a71fc0eea23e27f54b9ae240379c9e82a05d6fca73ecee13ca2e0e4d98390844697d8ed10715415c56152653edf460a47b70ddb868a03ee6a3f9840 /in:"dec_data" /out:aes.dec
**BLOB**
dwVersion : 00000001 - 1
guidProvider : {df9d8cd0-1501-11d1-8c7a-00c04fc297eb}
dwMasterKeyVersion : 00000001 - 1
[...]
* masterkey : ca4387eb0a71fc0eea23e27f54b9ae240379c9e82a05d6fca73ecee13ca2e0e4d98390844697d8ed10715415c56152653edf460a47b70ddb868a03ee6a3f9840
description :
Write to file 'aes.dec' is OK
Decrypting Login Data
aes.dec contains the decrypted encryption key. Now, we can decrypt the Login Data file. I made some modifications to this script to decrypt the Login Data file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
import os
import sys
from shutil import copy2
import sqlite3
from base64 import b64decode
from json import loads
import win32crypt
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import pandas as pd
def chrome_creds_extractor():
# Extract and decode the AES key which is used to
# encrypt the passwords.
# It is stored in '%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Local State'
# as JSON format
try:
key = open("aes.dec",'rb').read() #
except Exception as e:
print(e)
sys.exit(1)
# Copy sqlite chrome database since it cannot be accessed
# while chrome is running. It's location is
# '%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\default\Login Data'
try:
db_path = os.path.join("Login Data")
copy2(db_path,'chrome_db_temp.db')
conn = sqlite3.connect('chrome_db_temp.db')
c = conn.cursor()
# Query desired info from database
c.execute('select origin_url, action_url, username_value, password_value from logins')
data = []
for row in c.fetchall():
origin_url = row[0]
action_url = row[1]
username = row[2]
password = row[3]
# Get the initialization vector
iv = password[3:15]
password = password[15:]
# Generate cipher
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_GCM, iv)
# Decrypt password
password = cipher.decrypt(password)[:-16].decode()
print(f"Origin_url: {origin_url}\naction_url: {action_url}\nusername: {username}\npassword: {password}\n")
data.append([origin_url, action_url, username, password])
# Save result into Excel file
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["Origin URL", "Action URL", "Username", "Password"])
excel_path = 'chrome_creds.xlsx'
df.to_excel(excel_path, index=False)
# Apply formatting
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Font, Alignment, PatternFill
from openpyxl.worksheet.dimensions import ColumnDimension
wb = load_workbook(excel_path)
ws = wb.active
# Define colors for each column
colors = ["FFCCFF", "CCFFCC", "CCCCFF", "FFFFCC"]
# Enable text wrapping and set column width, colorize columns
for i, column in enumerate(ws.columns):
max_length = 0
column_letter = column[0].column_letter
for cell in column:
cell.alignment = Alignment(wrap_text=True)
cell.fill = PatternFill(start_color=colors[i % len(colors)], end_color=colors[i % len(colors)], fill_type="solid")
if len(str(cell.value)) > max_length:
max_length = len(str(cell.value))
ws.column_dimensions[column_letter].width = min(max_length + 2, 40)
# Apply bold font and background color to header
header_fill = PatternFill(start_color="FFFF00", end_color="FFFF00", fill_type="solid")
for cell in ws["1:1"]:
cell.font = Font(bold=True)
cell.fill = header_fill
# Freeze the top row
ws.freeze_panes = ws['A2']
wb.save(excel_path)
c.close()
conn.close()
os.remove('chrome_db_temp.db')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
sys.exit(1)
chrome_creds_extractor()
Ensure that you have required libraries installed:
1
pip install pycryptodome pandas openpyxl pypiwin32
It’s time to run the script:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C:\Users\sarp\Desktop\mimikatz-master\x64>python extract.py
Origin_url: https://mysecuresite.thm/
action_url:
username: Administrator
password: Sup3rPaS$w0rd1
Origin_url: https://worksite.thm/
action_url:
username: chrome
password: Sup3rSecuR3!
Finally, we have the credentials!
Questions
What is the first password that we find?
- Answer:
bubbles
What is the URL found in the first index? Fully defang the URL
- Answer:
hxxps[://]mysecuresite[.]thm/
What is the password found in the first index?
- Answer:
Sup3rPaS$w0rd1
What is the URL found in the second index? Fully defang the URL
- Answer:
hxxps[://]worksite[.]thm/
What is the password found in the second index?
- Answer:
Sup3rSecuR3!
Conclusion
A terrific room! Tinkering with DPAPI was a great experience. I learned a lot from this room. Thanks for reading! Feel free to reach out to me on Twitter if you have any questions.